mirror of
https://github.com/infiniflow/ragflow.git
synced 2025-12-29 16:05:35 +08:00
Docs: v0.23.0 release notes (#12251)
### What problem does this PR solve? ### Type of change - [x] Documentation Update --------- Co-authored-by: Yingfeng Zhang <yingfeng.zhang@gmail.com>
This commit is contained in:
48
docs/guides/dataset/auto_metadata.md
Normal file
48
docs/guides/dataset/auto_metadata.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
sidebar_position: -6
|
||||
slug: /auto_metadata
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Auto-extract metadata
|
||||
|
||||
Automatically extract metadata from uploaded files.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
RAGFlow v0.23.0 introduces the Auto-metadata feature, which uses large language models to automatically extract and generate metadata for files—eliminating the need for manual entry. In a typical RAG pipeline, metadata serves two key purposes:
|
||||
|
||||
- During the retrieval stage: Filters out irrelevant documents, narrowing the search scope to improve retrieval accuracy.
|
||||
- During the generation stage: If a text chunk is retrieved, its associated metadata is also passed to the LLM, providing richer contextual information about the source document to aid answer generation.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
:::danger WARNING
|
||||
Enabling TOC extraction requires significant memory, computational resources, and tokens.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Procedure
|
||||
|
||||
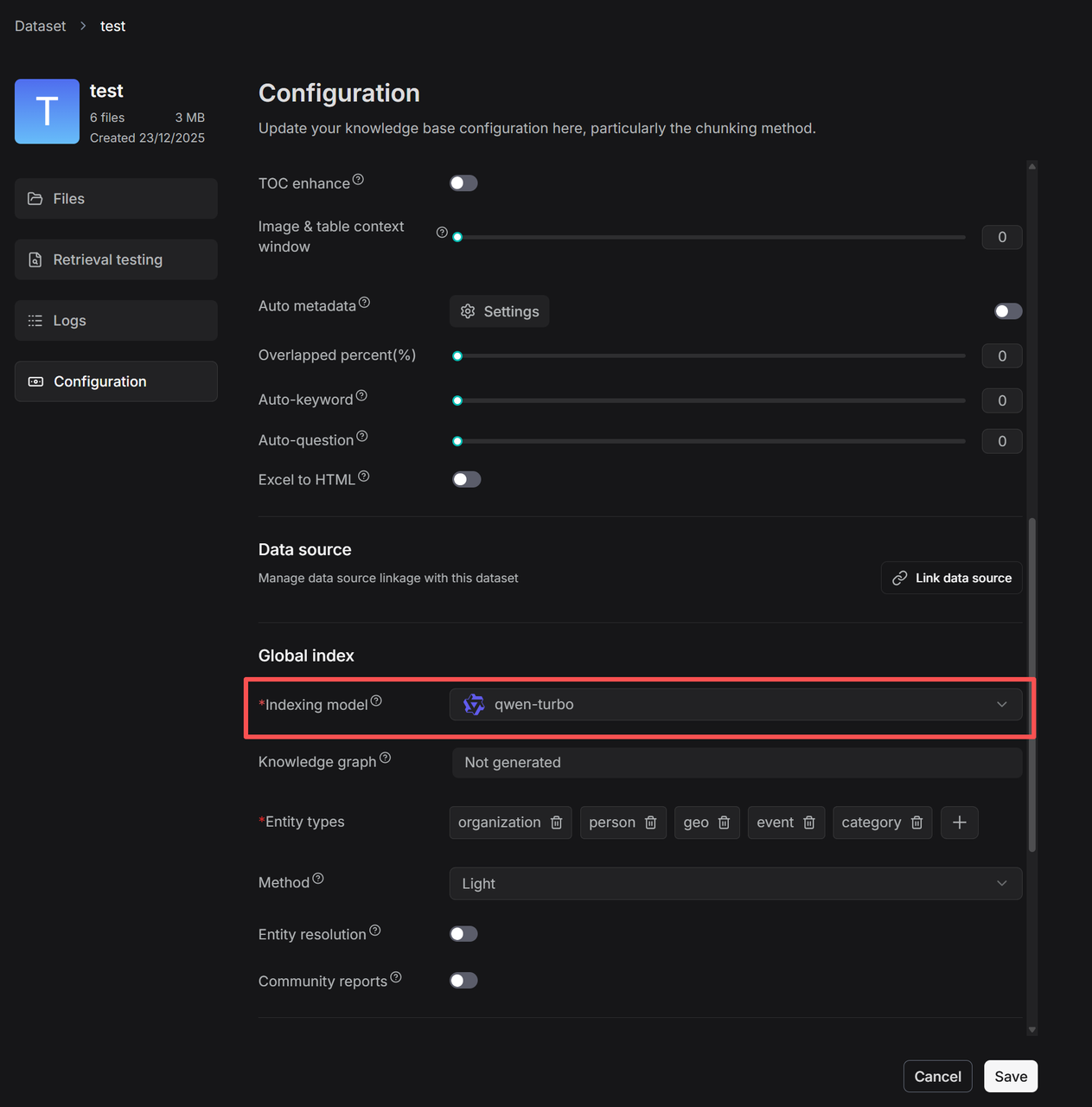
1. On your dataset's **Configuration** page, select an indexing model, which will be used to generate the knowledge graph, RAPTOR, auto-metadata, auto-keyword, and auto-question features for this dataset.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
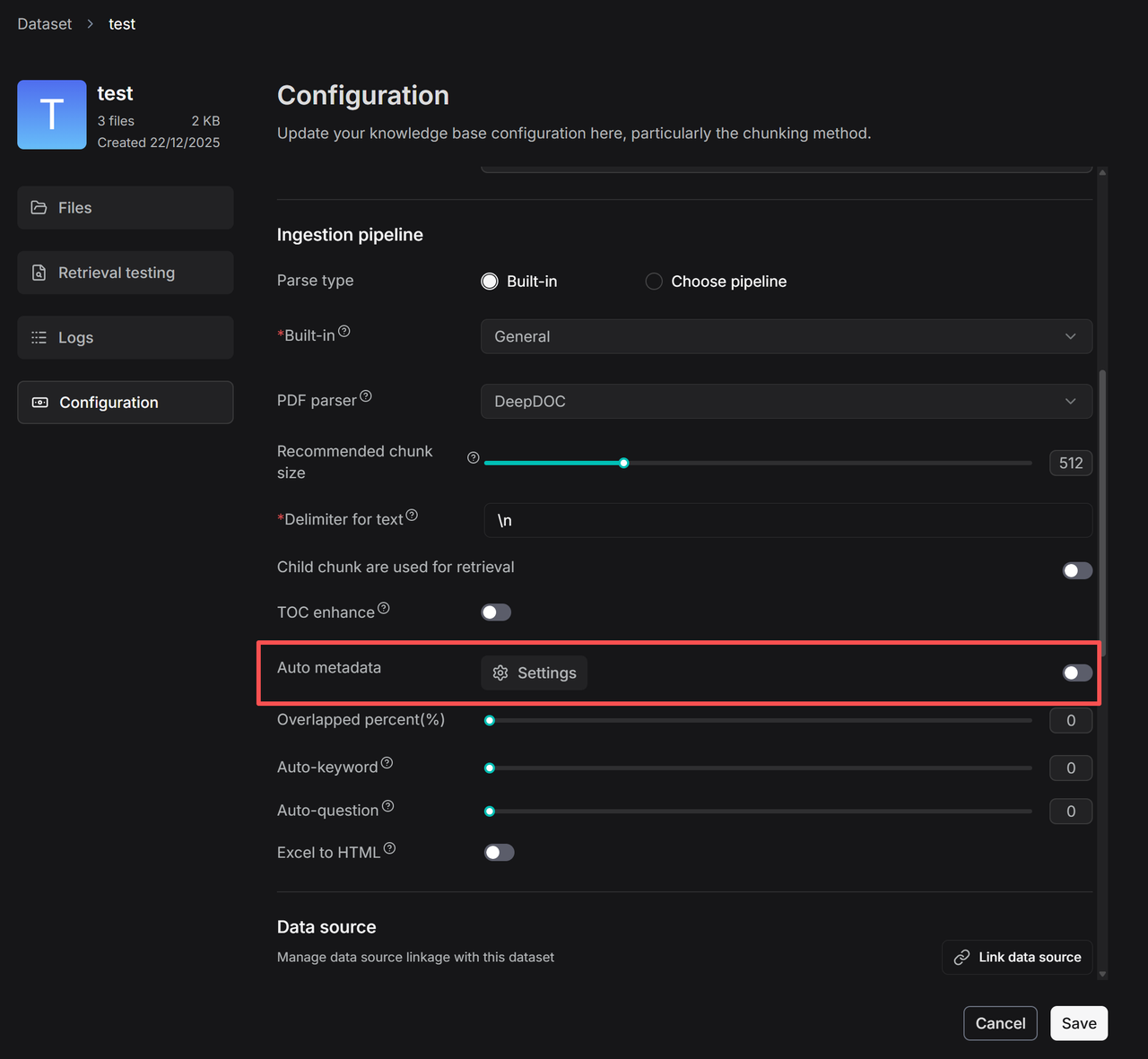
2. Click **Auto metadata** **>** **Settings** to go to the configuration page for automatic metadata generation rules.
|
||||
|
||||
_The configuration page for rules on automatically generating metadata appears._
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
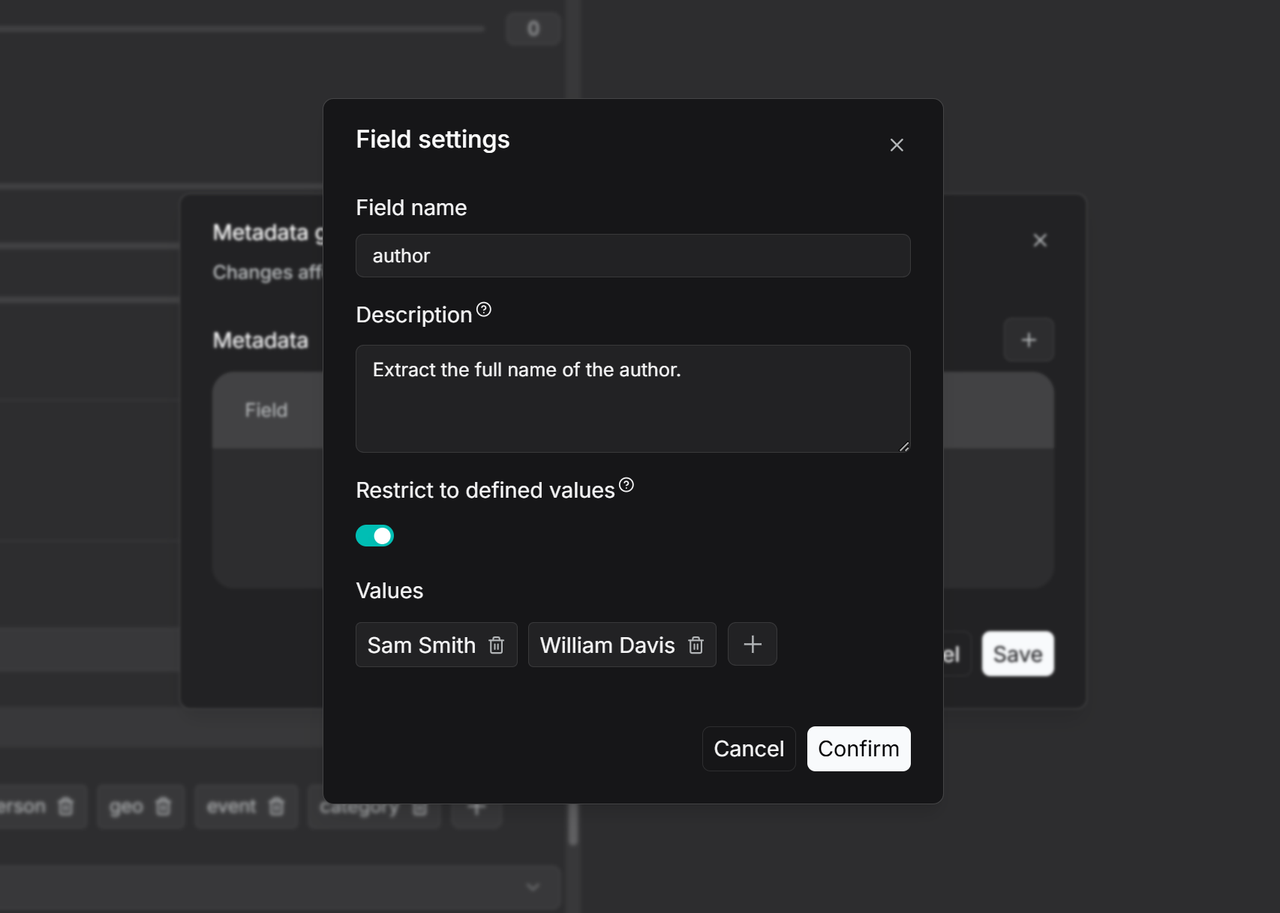
3. Click **+** to add new fields and enter the congiruation page.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
4. Enter a field name, such as Author, and add a description and examples in the Description section. This provides context to the large language model (LLM) for more accurate value extraction. If left blank, the LLM will extract values based only on the field name.
|
||||
|
||||
5. To restrict the LLM to generating metadata from a predefined list, enable the Restrict to defined values mode and manually add the allowed values. The LLM will then only generate results from this preset range.
|
||||
|
||||
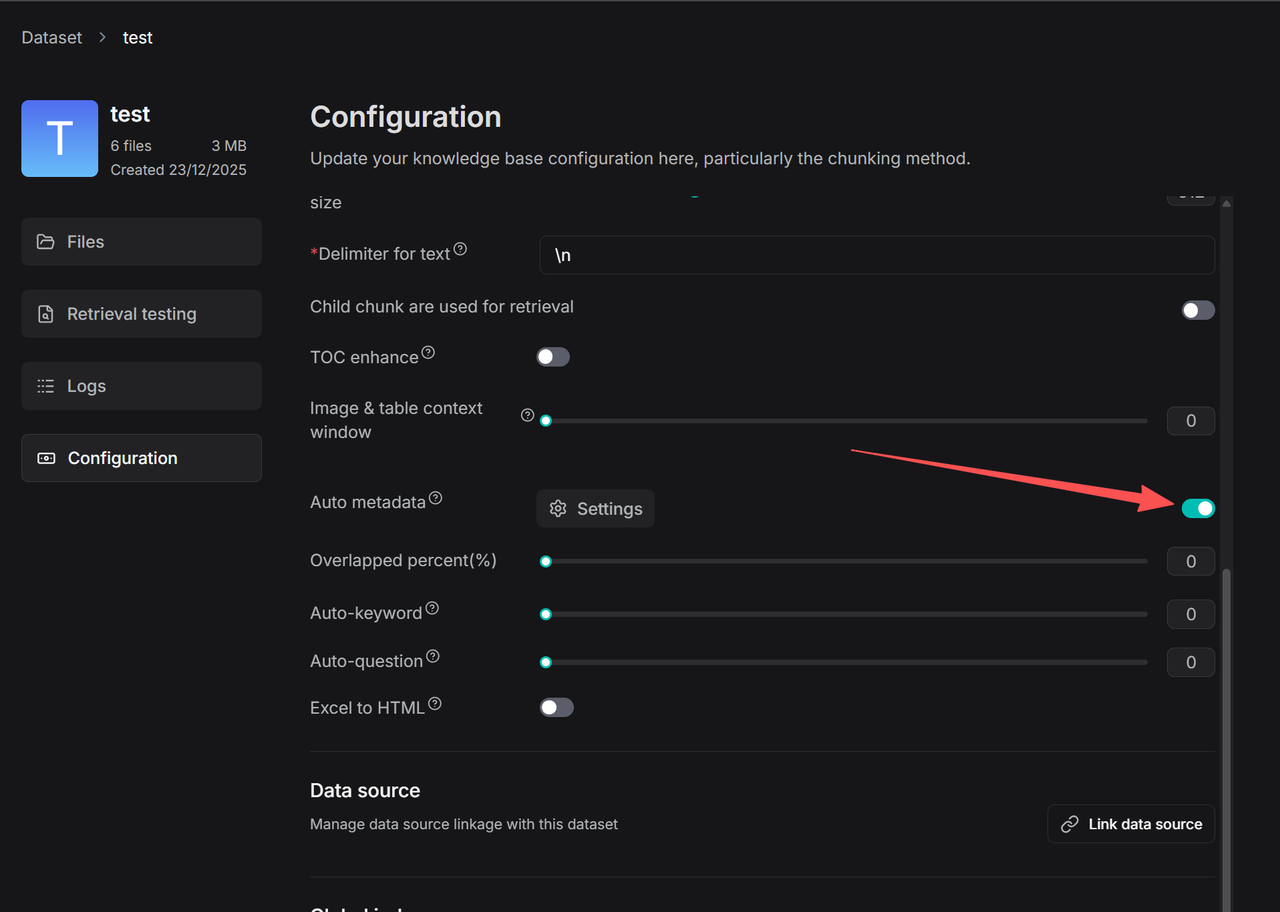
6. Once configured, turn on the Auto-metadata switch on the Configuration page. All newly uploaded files will have these rules applied during parsing. For files that have already been processed, you must re-parse them to trigger metadata generation. You can then use the filter function to check the metadata generation status of your files.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
34
docs/guides/dataset/configure_child_chunking_strategy.md
Normal file
34
docs/guides/dataset/configure_child_chunking_strategy.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
sidebar_position: -4
|
||||
slug: /configure_child_chunking_strategy
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Configure child chunking strategy
|
||||
|
||||
Set parent-child chunking strategy to improve retrieval.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
A persistent challenge in practical RAG applications lies in a structural tension within the traditional "chunk-embed-retrieve" pipeline: a single text chunk is tasked with both semantic matching (recall) and contextual understanding (utilization)—two inherently conflicting objectives. Recall demands fine-grained, precise chunks, while answer generation requires coherent, informationally complete context.
|
||||
|
||||
To resolve this tension, RAGFlow previously introduced the Table of Contents (TOC) enhancement feature, which uses a large language model (LLM) to generate document structure and automatically supplements missing context during retrieval based on that TOC. In version 0.23.0, this capability has been systematically integrated into the Ingestion Pipeline, and a novel parent-child chunking mechanism has been introduced.
|
||||
|
||||
Under this mechanism, a document is first segmented into larger parent chunks, each maintaining a relatively complete semantic unit to ensure logical and background integrity. Each parent chunk can then be further subdivided into multiple child chunks for precise recall. During retrieval, the system first locates the most relevant text segments based on the child chunks while automatically associating and recalling their parent chunk. This approach maintains high recall relevance while providing ample semantic background for the generation phase.
|
||||
|
||||
For instance, when processing a *Compliance Handbook*, a user query about "liability for breach" might precisely retrieve a child chunk stating, "The penalty for breach is 20% of the total contract value," but without context, it cannot clarify whether this clause applies to "minor breach" or "material breach." Leveraging the parent-child chunking mechanism, the system returns this child chunk along with its parent chunk, which contains the complete section of the clause. This allows the LLM to make accurate judgments based on broader context, avoiding misinterpretation.
|
||||
|
||||
Through this dual-layer structure of "precise localization + contextual supplementation," RAGFlow ensures retrieval accuracy while significantly enhancing the reliability and completeness of generated answers.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Procedure
|
||||
|
||||
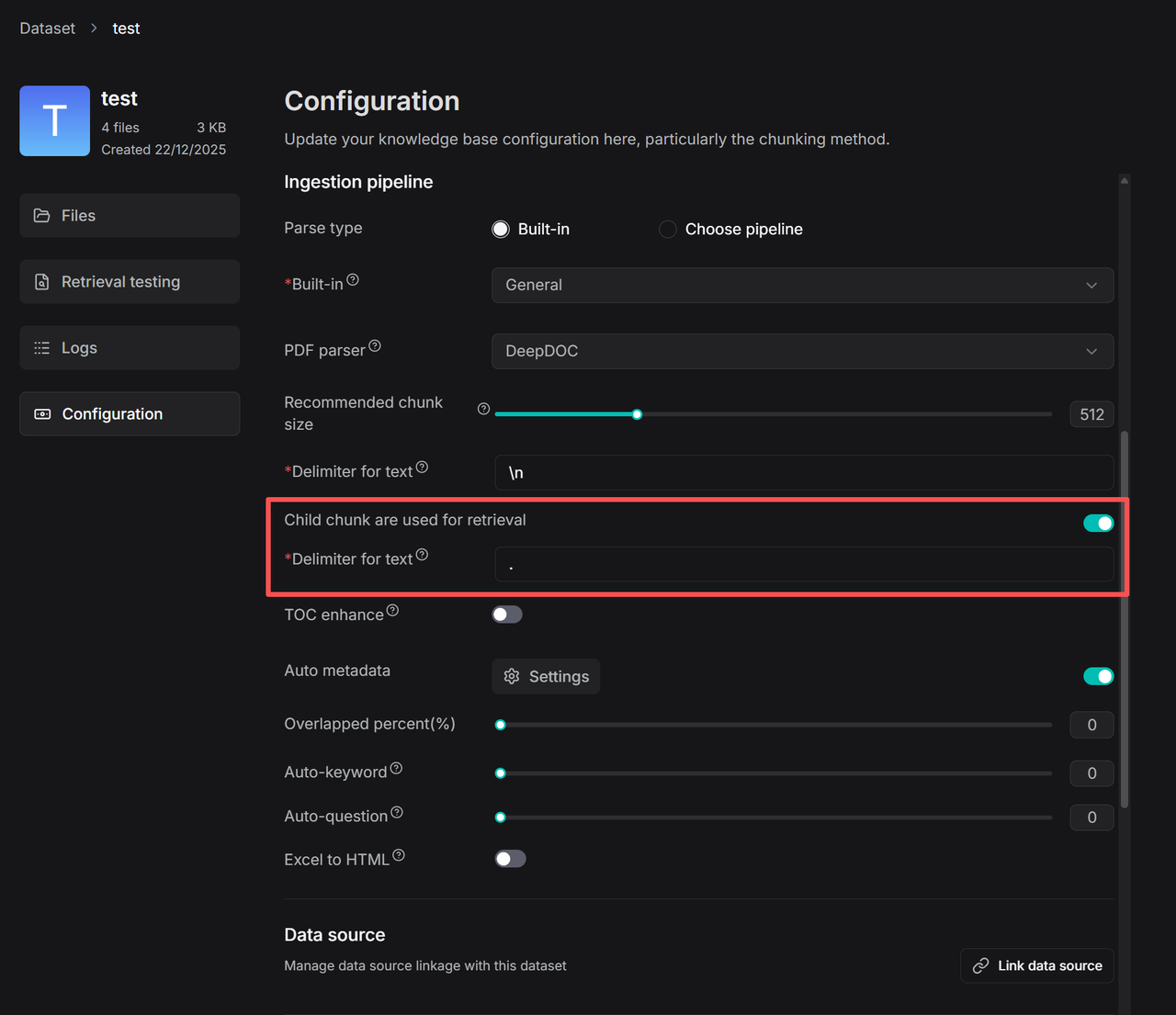
1. On your dataset's **Configuration** page, find the **Child chunk are used for retrieval** toggle:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
2. Set the delimiter for child chunks.
|
||||
|
||||
3. This configuration applies to the **Chunker** component when it comes to ingestion pipeline settings:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
47
docs/guides/dataset/manage_metadata.md
Normal file
47
docs/guides/dataset/manage_metadata.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
sidebar_position: -5
|
||||
slug: /manage_metadata
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Manage metadata
|
||||
|
||||
Manage metadata for your dataset and for your individual documents.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
From v0.23.0 onwards, RAGFlow allows you to manage metadata both at the dataset level and for individual files.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Procedure
|
||||
|
||||
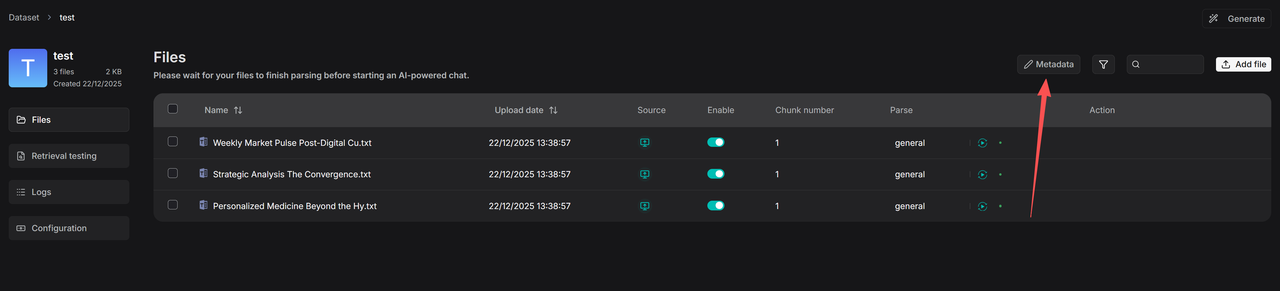
1. Click on **Metadata** within your dataset to access the **Manage Metadata** page.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
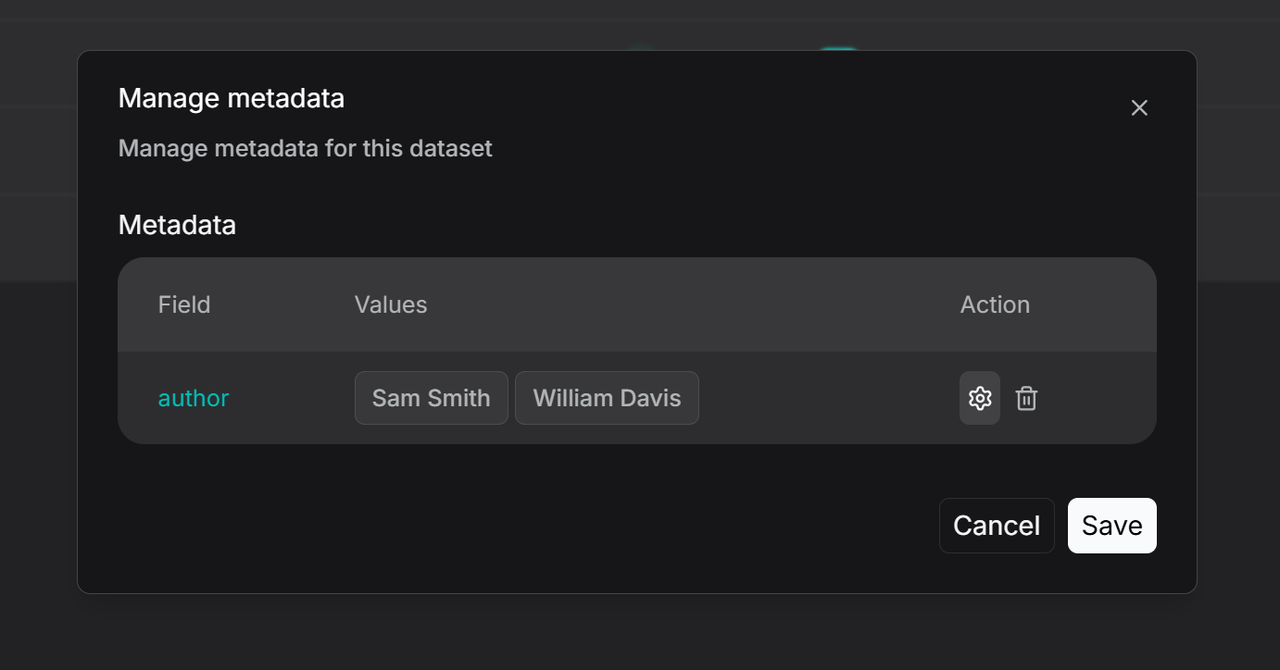
2. On the **Manage Metadata** page, you can do either of the following:
|
||||
- Edit Values: You can modify existing values. If you rename two values to be identical, they will be automatically merged.
|
||||
- Delete: You can delete specific values or entire fields. These changes will apply to all associated files.
|
||||
|
||||
_The configuration page for rules on automatically generating metadata appears._
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
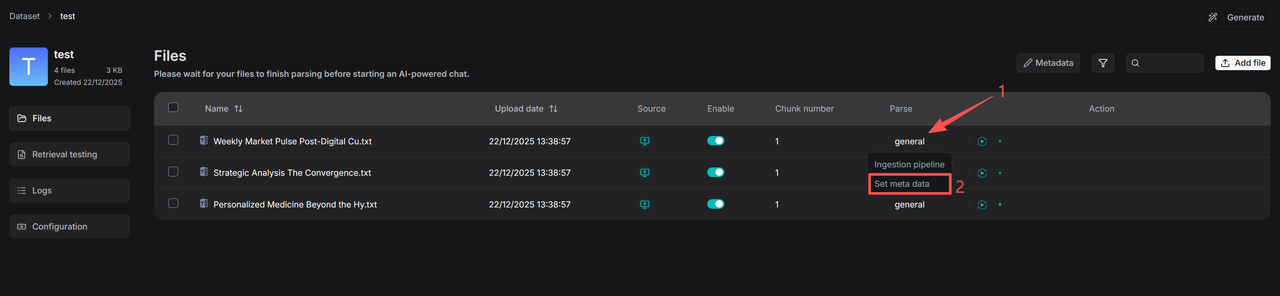
3. To manage metadata for a single file, navigate to the file's details page as shown below. Click on the parsing method (e.g., **General**), then select **Set Metadata** to view or edit the file's metadata. Here, you can add, delete, or modify metadata fields for this specific file. Any edits made here will be reflected in the global statistics on the main Metadata management page for the knowledge base.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
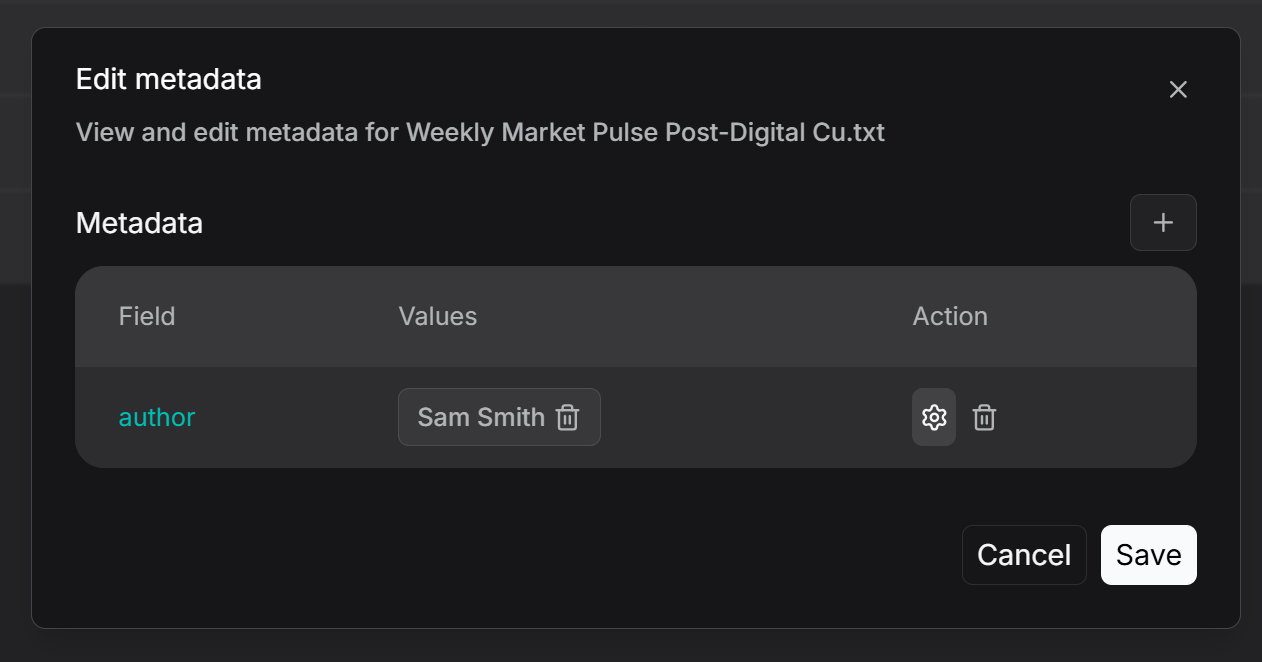
|
||||
|
||||
4. The filtering function operates at two levels: knowledge base management and retrieval. Within the dataset, click the Filter button to view the number of files associated with each value under existing metadata fields. By selecting specific values, you can display all linked files.
|
||||
|
||||
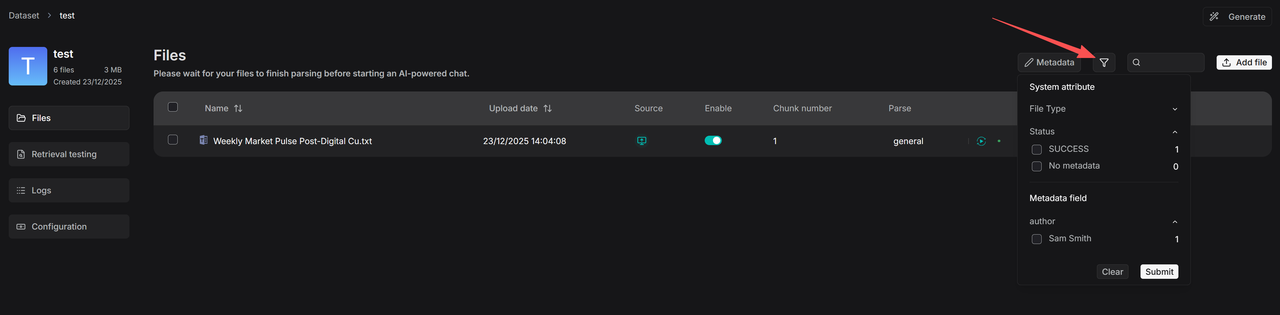
|
||||
|
||||
5. Metadata filtering is also supported during the retrieval stage. In Chat, for example, you can set metadata filtering rules after configuring a knowledge base:
|
||||
|
||||
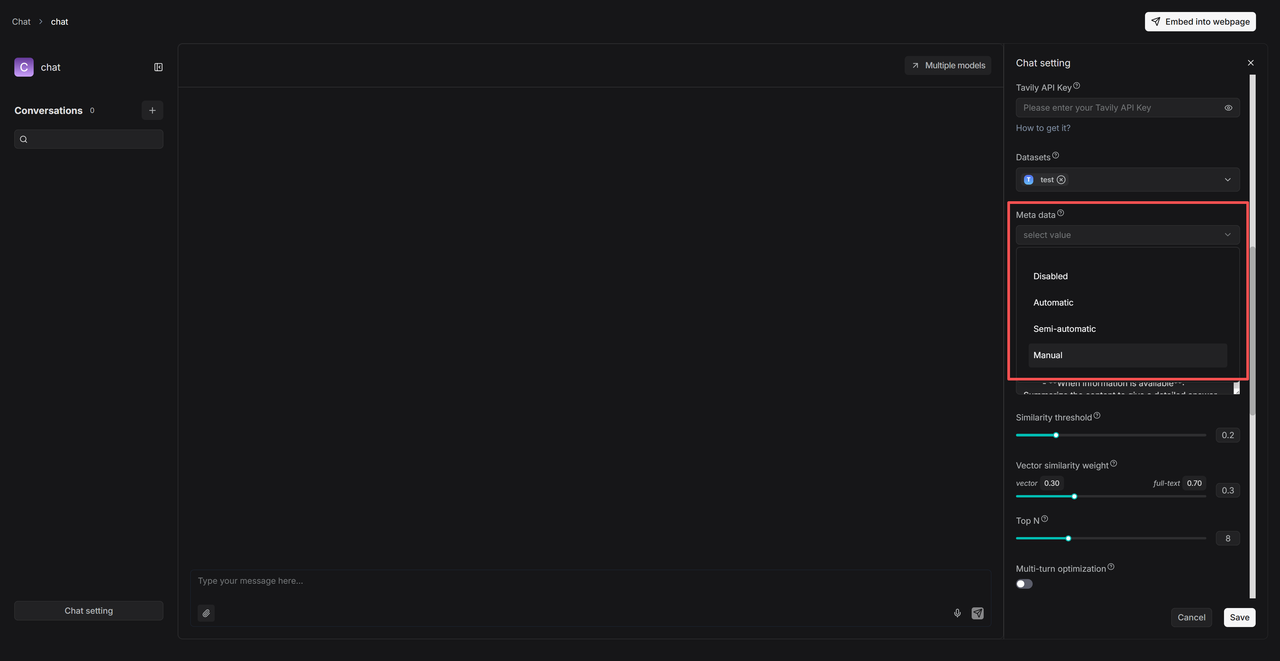
|
||||
|
||||
- **Automatic** Mode: The system automatically filters documents based on the user's query and the existing metadata in the knowledge base.
|
||||
- **Semi-automatic** Mode: Users first define the filtering scope at the field level (e.g., for **Author**), and then the system automatically filters within that preset range.
|
||||
- **Manual** Mode: Users manually set precise, value-specific filter conditions, supported by operators such as **Equals**, **Not equals**, **In**, **Not in**, and more.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
sidebar_position: -4
|
||||
sidebar_position: -3
|
||||
slug: /select_pdf_parser
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
25
docs/guides/dataset/set_context_window.md
Normal file
25
docs/guides/dataset/set_context_window.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
sidebar_position: -8
|
||||
slug: /set_context_window
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Set context window size
|
||||
|
||||
Set context window size for images and tables to improve long-context RAG performances.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
RAGFlow leverages built-in DeepDoc, along with external document models like MinerU and Docling, to parse document layouts. In previous versions, images and tables extracted based on document layout were treated as independent chunks. Consequently, if a search query did not directly match the content of an image or table, these elements would not be retrieved. However, real-world documents frequently interweave charts and tables with surrounding text, which often describes them. Therefore, recalling charts based on this contextual text is an essential capability.
|
||||
|
||||
To address this, RAGFlow 0.23.0 introduces the **Image & table context window** feature. Inspired by key principles of the research-focused, open-source multimodal RAG project RAG-Anything, this functionality allows surrounding text and adjacent visuals to be grouped into a single chunk based on a user-configurable window size. This ensures they are retrieved together, significantly improving the recall accuracy for charts and tables.
|
||||
|
||||
## Procedure
|
||||
|
||||
1. On your dataset's **Configuration** page, find the **Image & table context window** slider:
|
||||
|
||||
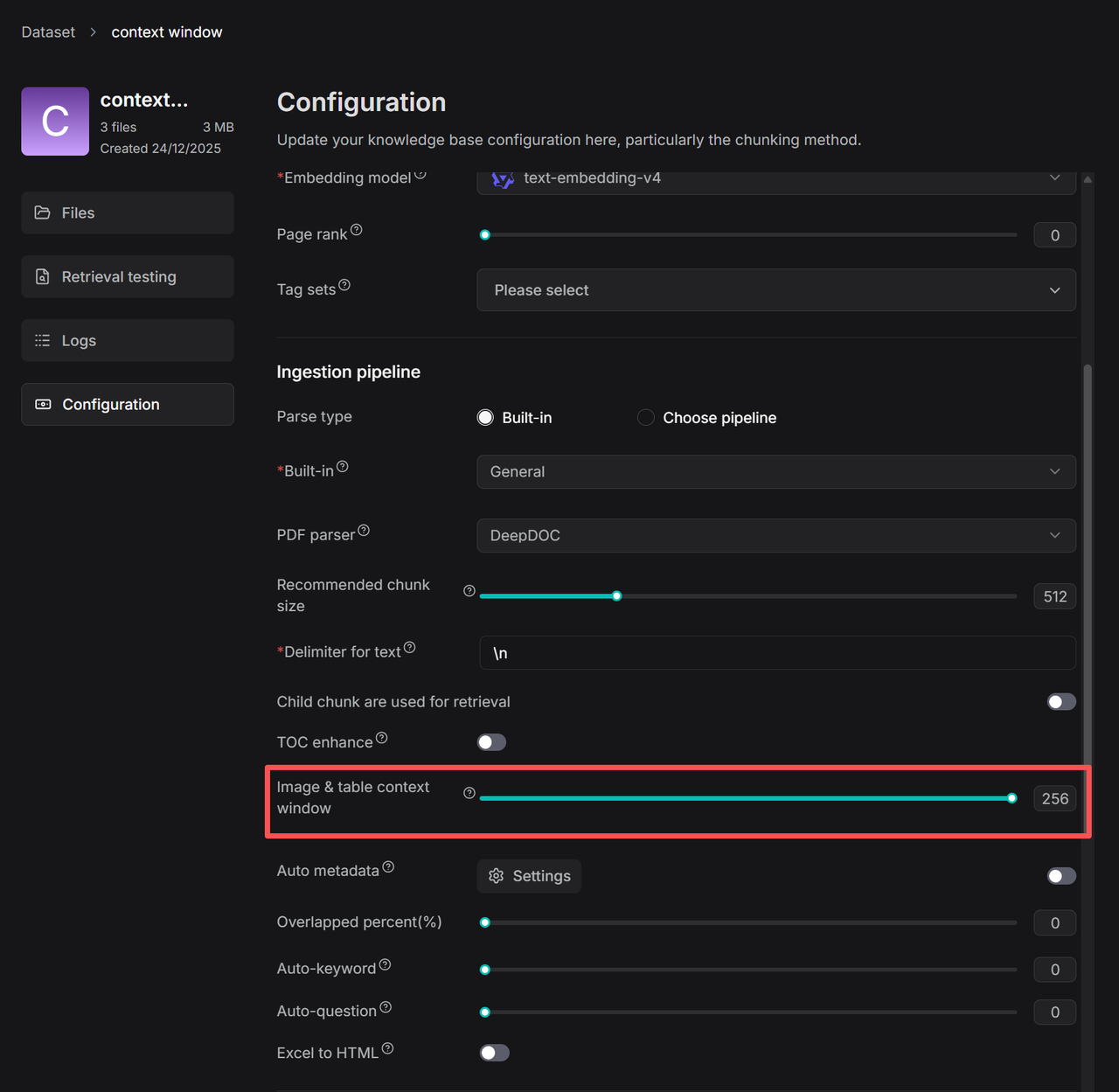
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
2. Adjust the number of context tokens according to your needs.
|
||||
|
||||
*The number in the red box indicates that approximately **N tokens** of text from above and below the image/table will be captured and inserted into the image or table chunk as contextual information. The capture process intelligently optimizes boundaries at punctuation marks to preserve semantic integrity. *
|
||||
@ -5,7 +5,7 @@ slug: /set_metadata
|
||||
|
||||
# Set metadata
|
||||
|
||||
Add metadata to an uploaded file
|
||||
Manually add metadata to an uploaded file
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
@ -29,4 +29,4 @@ Ensure that your metadata is in JSON format; otherwise, your updates will not be
|
||||
|
||||
### Can I set metadata for multiple documents at once?
|
||||
|
||||
No, you must set metadata *individually* for each document, as RAGFlow does not support batch setting of metadata. If you still consider this feature essential, please [raise an issue](https://github.com/infiniflow/ragflow/issues) explaining your use case and its importance.
|
||||
From v0.23.0 onwards, you can set metadata for each document individually or have the LLM auto-generate metadata for multiple files. See [Extract metadata](./auto_metadata.md) for details.
|
||||
@ -7,6 +7,61 @@ slug: /release_notes
|
||||
|
||||
Key features, improvements and bug fixes in the latest releases.
|
||||
|
||||
## v0.23.0
|
||||
|
||||
Released on December 29, 2025.
|
||||
|
||||
### New features
|
||||
|
||||
- Memory
|
||||
- Implements a **Memory** interface for managing memory.
|
||||
- Supports configuring context via the **Retrieval** or **Message** component.
|
||||
- Agent
|
||||
- Improves the **Agent** component's performance by refactoring the underlying architecture.
|
||||
- The **Agent** component can now output structured data for use in downstream components.
|
||||
- Supports using webhook to trigger agent execution.
|
||||
- Supports voice input/output.
|
||||
- Supports configuring multiple **Retrieval** components per **Agent** component.
|
||||
- Ingestion pipeline
|
||||
- Supports extracting table of contents in the **Transformer** component to improve long-context RAG performance.
|
||||
- Dataset
|
||||
- Supports configuring context window for images and tables.
|
||||
- Introduces parent-child chunking strategy.
|
||||
- Supports auto-generation of metadata during file parsing.
|
||||
- Chat: Supports voice input.
|
||||
|
||||
### Improvements
|
||||
|
||||
- Bumps RAGFlow's document engine, [Infinity](https://github.com/infiniflow/infinity) to v0.6.13 (backward compatible).
|
||||
|
||||
### Data sources
|
||||
|
||||
- Google Cloud Storage
|
||||
- Gmail
|
||||
- Dropbox
|
||||
- WebDAV
|
||||
- Airtable
|
||||
|
||||
### Model support
|
||||
|
||||
- GPT-5.2
|
||||
- GPT-5.2 Pro
|
||||
- GPT-5.1
|
||||
- GPT-5.1 Instant
|
||||
- Claude Opus 4.5
|
||||
- MiniMax M2
|
||||
- GLM-4.7.
|
||||
- A MinerU configuration interface.
|
||||
- AI Badgr (model provider).
|
||||
|
||||
### API changes
|
||||
|
||||
#### HTTP API
|
||||
|
||||
- [Converse with Agent](./references/http_api_reference.md#converse-with-agent) returns complete execution trace logs.
|
||||
- [Create chat completion](./references/http_api_reference.md#create-chat-completion) supports metadata-based filtering.
|
||||
- [Converse with chat assistant](./references/http_api_reference.md#converse-with-chat-assistant) supports metadata-based filtering.
|
||||
|
||||
## v0.22.1
|
||||
|
||||
Released on November 19, 2025.
|
||||
|
||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user