mirror of
https://github.com/infiniflow/ragflow.git
synced 2026-02-04 01:25:07 +08:00
Fix: Merge main branch (#10377)
### What problem does this PR solve? ### Type of change - [x] Bug Fix (non-breaking change which fixes an issue) --------- Signed-off-by: dependabot[bot] <support@github.com> Signed-off-by: jinhai <haijin.chn@gmail.com> Signed-off-by: Jin Hai <haijin.chn@gmail.com> Co-authored-by: Lynn <lynn_inf@hotmail.com> Co-authored-by: chanx <1243304602@qq.com> Co-authored-by: balibabu <cike8899@users.noreply.github.com> Co-authored-by: 纷繁下的无奈 <zhileihuang@126.com> Co-authored-by: huangzl <huangzl@shinemo.com> Co-authored-by: writinwaters <93570324+writinwaters@users.noreply.github.com> Co-authored-by: Wilmer <33392318@qq.com> Co-authored-by: Adrian Weidig <adrianweidig@gmx.net> Co-authored-by: Zhichang Yu <yuzhichang@gmail.com> Co-authored-by: Copilot <175728472+Copilot@users.noreply.github.com> Co-authored-by: Yongteng Lei <yongtengrey@outlook.com> Co-authored-by: Liu An <asiro@qq.com> Co-authored-by: buua436 <66937541+buua436@users.noreply.github.com> Co-authored-by: BadwomanCraZY <511528396@qq.com> Co-authored-by: cucusenok <31804608+cucusenok@users.noreply.github.com> Co-authored-by: Russell Valentine <russ@coldstonelabs.org> Co-authored-by: dependabot[bot] <49699333+dependabot[bot]@users.noreply.github.com> Co-authored-by: Billy Bao <newyorkupperbay@gmail.com> Co-authored-by: Zhedong Cen <cenzhedong2@126.com> Co-authored-by: TensorNull <129579691+TensorNull@users.noreply.github.com> Co-authored-by: TensorNull <tensor.null@gmail.com> Co-authored-by: Ajay <160579663+aybanda@users.noreply.github.com> Co-authored-by: AB <aj@Ajays-MacBook-Air.local> Co-authored-by: 天海蒼灆 <huangaoqin@tecpie.com> Co-authored-by: He Wang <wanghechn@qq.com> Co-authored-by: Atsushi Hatakeyama <atu729@icloud.com> Co-authored-by: Jin Hai <haijin.chn@gmail.com> Co-authored-by: Mohamed Mathari <155896313+melmathari@users.noreply.github.com> Co-authored-by: Mohamed Mathari <nocodeventure@Mac-mini-van-Mohamed.fritz.box> Co-authored-by: Stephen Hu <stephenhu@seismic.com> Co-authored-by: Shaun Zhang <zhangwfjh@users.noreply.github.com> Co-authored-by: zhimeng123 <60221886+zhimeng123@users.noreply.github.com> Co-authored-by: mxc <mxc@example.com> Co-authored-by: Dominik Novotný <50611433+SgtMarmite@users.noreply.github.com> Co-authored-by: EVGENY M <168018528+rjohny55@users.noreply.github.com> Co-authored-by: mcoder6425 <mcoder64@gmail.com> Co-authored-by: TeslaZY <TeslaZY@outlook.com> Co-authored-by: lemsn <lemsn@msn.com> Co-authored-by: lemsn <lemsn@126.com> Co-authored-by: Adrian Gora <47756404+adagora@users.noreply.github.com> Co-authored-by: Womsxd <45663319+Womsxd@users.noreply.github.com> Co-authored-by: FatMii <39074672+FatMii@users.noreply.github.com>
This commit is contained in:
@ -229,18 +229,4 @@ The global variable name for the output of the **Agent** component, which can be
|
||||
|
||||
### Why does it take so long for my Agent to respond?
|
||||
|
||||
An Agent’s response time generally depends on two key factors: the LLM’s capabilities and the prompt, the latter reflecting task complexity. When using an Agent, you should always balance task demands with the LLM’s ability. See [How to balance task complexity with an Agent's performance and speed?](#how-to-balance-task-complexity-with-an-agents-performance-and-speed) for details.
|
||||
|
||||
## Best practices
|
||||
|
||||
### How to balance task complexity with an Agent’s performance and speed?
|
||||
|
||||
- For simple tasks, such as retrieval, rewriting, formatting, or structured data extraction, use concise prompts, remove planning or reasoning instructions, enforce output length limits, and select smaller or Turbo-class models. This significantly reduces latency and cost with minimal impact on quality.
|
||||
|
||||
- For complex tasks, like multi-step reasoning, cross-document synthesis, or tool-based workflows, maintain or enhance prompts that include planning, reflection, and verification steps.
|
||||
|
||||
- In multi-Agent orchestration systems, delegate simple subtasks to sub-Agents using smaller, faster models, and reserve more powerful models for the lead Agent to handle complexity and uncertainty.
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip KEY INSIGHT
|
||||
Focus on minimizing output tokens — through summarization, bullet points, or explicit length limits — as this has far greater impact on reducing latency than optimizing input size.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
See [here](../best_practices/accelerate_agent_question_answering.md) for details.
|
||||
@ -67,14 +67,14 @@ You can tune document parsing and embedding efficiency by setting the environmen
|
||||
|
||||
## Frequently asked questions
|
||||
|
||||
### Is the uploaded file in a knowledge base?
|
||||
### Is the uploaded file in a dataset?
|
||||
|
||||
No. Files uploaded to an agent as input are not stored in a knowledge base and hence will not be processed using RAGFlow's built-in OCR, DLR or TSR models, or chunked using RAGFlow's built-in chunking methods.
|
||||
No. Files uploaded to an agent as input are not stored in a dataset and hence will not be processed using RAGFlow's built-in OCR, DLR or TSR models, or chunked using RAGFlow's built-in chunking methods.
|
||||
|
||||
### File size limit for an uploaded file
|
||||
|
||||
There is no _specific_ file size limit for a file uploaded to an agent. However, note that model providers typically have a default or explicit maximum token setting, which can range from 8196 to 128k: The plain text part of the uploaded file will be passed in as the key value, but if the file's token count exceeds this limit, the string will be truncated and incomplete.
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip NOTE
|
||||
The variables `MAX_CONTENT_LENGTH` in `/docker/.env` and `client_max_body_size` in `/docker/nginx/nginx.conf` set the file size limit for each upload to a knowledge base or **File Management**. These settings DO NOT apply in this scenario.
|
||||
The variables `MAX_CONTENT_LENGTH` in `/docker/.env` and `client_max_body_size` in `/docker/nginx/nginx.conf` set the file size limit for each upload to a dataset or **File Management**. These settings DO NOT apply in this scenario.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
@ -49,6 +49,10 @@ You can specify multiple input sources for the **Code** component. Click **+ Add
|
||||
|
||||
This field allows you to enter and edit your source code.
|
||||
|
||||
:::danger IMPORTANT
|
||||
If your code implementation includes defined variables, whether input or output variables, ensure they are also specified in the corresponding **Input** or **Output** sections.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
#### A Python code example
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
@ -77,6 +81,15 @@ This field allows you to enter and edit your source code.
|
||||
|
||||
You define the output variable(s) of the **Code** component here.
|
||||
|
||||
:::danger IMPORTANT
|
||||
If you define output variables here, ensure they are also defined in your code implementation; otherwise, their values will be `null`. The following are two examples:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
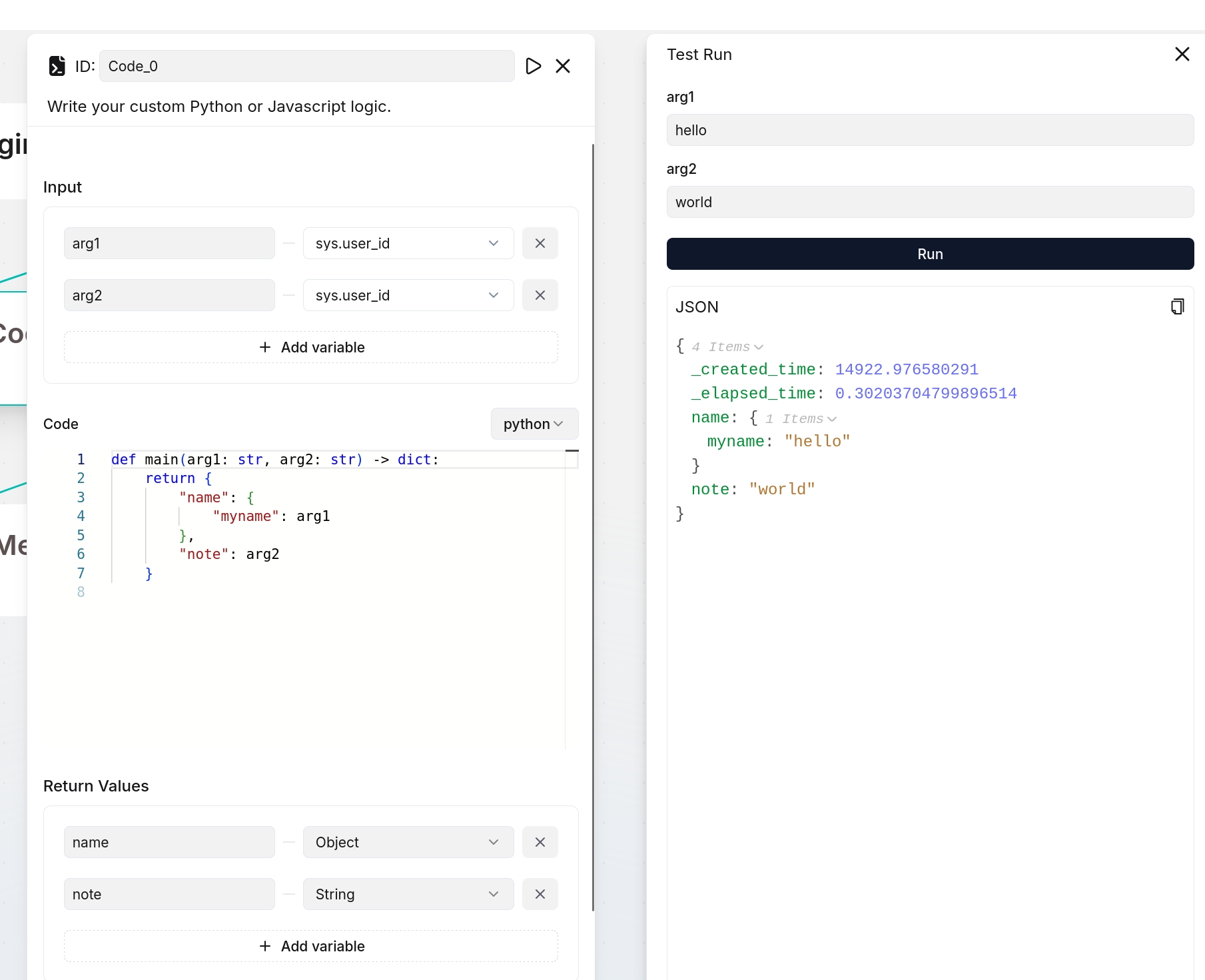
|
||||
|
||||
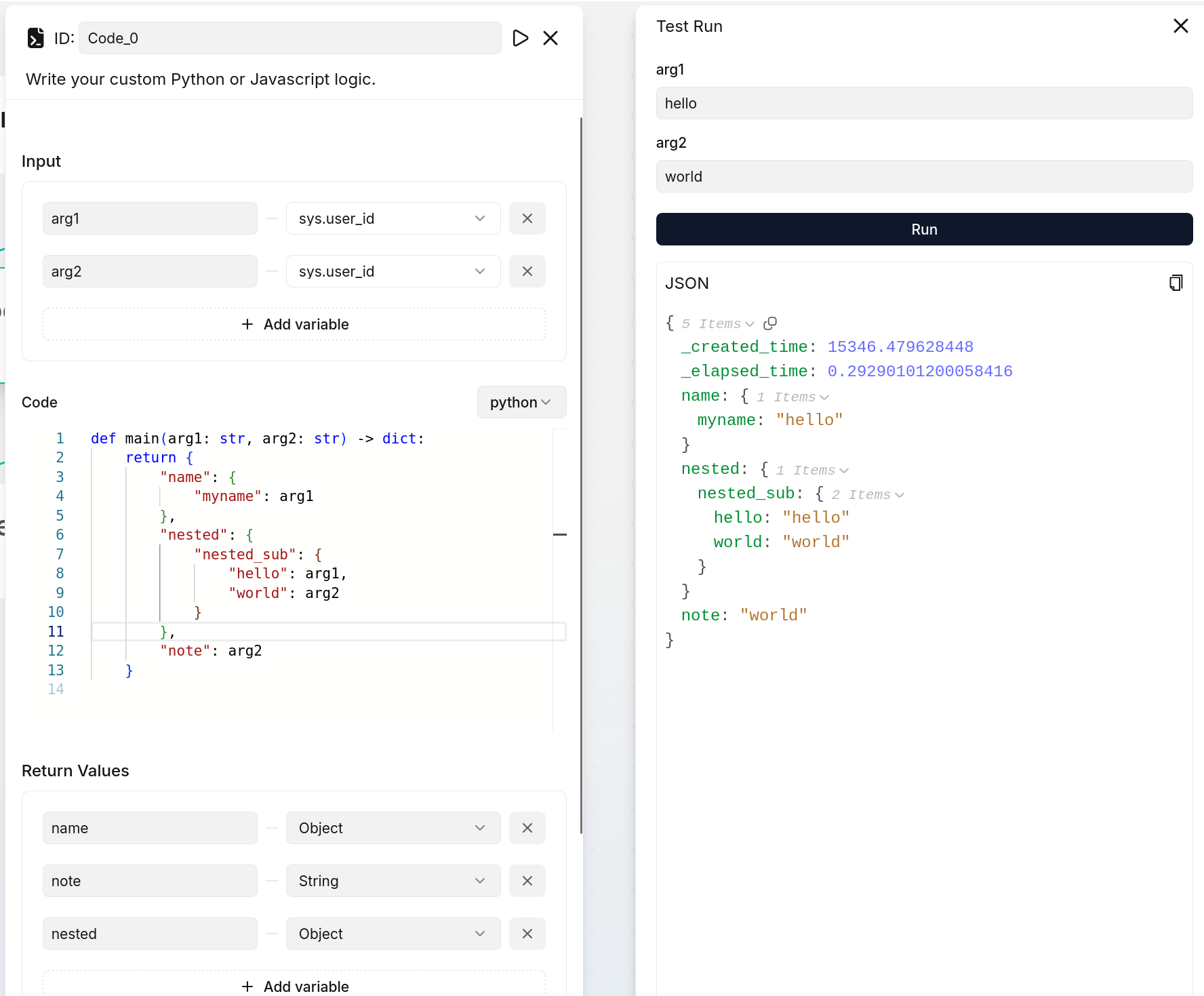
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### Output
|
||||
|
||||
The defined output variable(s) will be auto-populated here.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -9,7 +9,7 @@ A component that retrieves information from specified datasets.
|
||||
|
||||
## Scenarios
|
||||
|
||||
A **Retrieval** component is essential in most RAG scenarios, where information is extracted from designated knowledge bases before being sent to the LLM for content generation. A **Retrieval** component can operate either as a standalone workflow module or as a tool for an **Agent** component. In the latter role, the **Agent** component has autonomous control over when to invoke it for query and retrieval.
|
||||
A **Retrieval** component is essential in most RAG scenarios, where information is extracted from designated datasets before being sent to the LLM for content generation. A **Retrieval** component can operate either as a standalone workflow module or as a tool for an **Agent** component. In the latter role, the **Agent** component has autonomous control over when to invoke it for query and retrieval.
|
||||
|
||||
The following screenshot shows a reference design using the **Retrieval** component, where the component serves as a tool for an **Agent** component. You can find it from the **Report Agent Using Knowledge Base** Agent template.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -17,7 +17,7 @@ The following screenshot shows a reference design using the **Retrieval** compon
|
||||
|
||||
## Prerequisites
|
||||
|
||||
Ensure you [have properly configured your target knowledge base(s)](../../dataset/configure_knowledge_base.md).
|
||||
Ensure you [have properly configured your target dataset(s)](../../dataset/configure_knowledge_base.md).
|
||||
|
||||
## Quickstart
|
||||
|
||||
@ -36,9 +36,9 @@ The **Retrieval** component depends on query variables to specify its queries.
|
||||
|
||||
By default, you can use `sys.query`, which is the user query and the default output of the **Begin** component. All global variables defined before the **Retrieval** component can also be used as query statements. Use the `(x)` button or type `/` to show all the available query variables.
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Select knowledge base(s) to query
|
||||
### 3. Select dataset(s) to query
|
||||
|
||||
You can specify one or multiple knowledge bases to retrieve data from. If selecting mutiple, ensure they use the same embedding model.
|
||||
You can specify one or multiple datasets to retrieve data from. If selecting mutiple, ensure they use the same embedding model.
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. Expand **Advanced Settings** to configure the retrieval method
|
||||
|
||||
@ -52,7 +52,7 @@ Using a rerank model will *significantly* increase the system's response time. I
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. Enable cross-language search
|
||||
|
||||
If your user query is different from the languages of the knowledge bases, you can select the target languages in the **Cross-language search** dropdown menu. The model will then translates queries to ensure accurate matching of semantic meaning across languages.
|
||||
If your user query is different from the languages of the datasets, you can select the target languages in the **Cross-language search** dropdown menu. The model will then translates queries to ensure accurate matching of semantic meaning across languages.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. Test retrieval results
|
||||
@ -76,10 +76,10 @@ The **Retrieval** component relies on query variables to specify its queries. Al
|
||||
|
||||
### Knowledge bases
|
||||
|
||||
Select the knowledge base(s) to retrieve data from.
|
||||
Select the dataset(s) to retrieve data from.
|
||||
|
||||
- If no knowledge base is selected, meaning conversations with the agent will not be based on any knowledge base, ensure that the **Empty response** field is left blank to avoid an error.
|
||||
- If you select multiple knowledge bases, you must ensure that the knowledge bases (datasets) you select use the same embedding model; otherwise, an error message would occur.
|
||||
- If no dataset is selected, meaning conversations with the agent will not be based on any dataset, ensure that the **Empty response** field is left blank to avoid an error.
|
||||
- If you select multiple datasets, you must ensure that the datasets you select use the same embedding model; otherwise, an error message would occur.
|
||||
|
||||
### Similarity threshold
|
||||
|
||||
@ -110,11 +110,11 @@ Using a rerank model will *significantly* increase the system's response time.
|
||||
|
||||
### Empty response
|
||||
|
||||
- Set this as a response if no results are retrieved from the knowledge base(s) for your query, or
|
||||
- Set this as a response if no results are retrieved from the dataset(s) for your query, or
|
||||
- Leave this field blank to allow the chat model to improvise when nothing is found.
|
||||
|
||||
:::caution WARNING
|
||||
If you do not specify a knowledge base, you must leave this field blank; otherwise, an error would occur.
|
||||
If you do not specify a dataset, you must leave this field blank; otherwise, an error would occur.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### Cross-language search
|
||||
@ -124,10 +124,10 @@ Select one or more languages for cross‑language search. If no language is sele
|
||||
### Use knowledge graph
|
||||
|
||||
:::caution IMPORTANT
|
||||
Before enabling this feature, ensure you have properly [constructed a knowledge graph from each target knowledge base](../../dataset/construct_knowledge_graph.md).
|
||||
Before enabling this feature, ensure you have properly [constructed a knowledge graph from each target dataset](../../dataset/construct_knowledge_graph.md).
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
Whether to use knowledge graph(s) in the specified knowledge base(s) during retrieval for multi-hop question answering. When enabled, this would involve iterative searches across entity, relationship, and community report chunks, greatly increasing retrieval time.
|
||||
Whether to use knowledge graph(s) in the specified dataset(s) during retrieval for multi-hop question answering. When enabled, this would involve iterative searches across entity, relationship, and community report chunks, greatly increasing retrieval time.
|
||||
|
||||
### Output
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -27,7 +27,7 @@ Agents and RAG are complementary techniques, each enhancing the other’s capabi
|
||||
Before proceeding, ensure that:
|
||||
|
||||
1. You have properly set the LLM to use. See the guides on [Configure your API key](../models/llm_api_key_setup.md) or [Deploy a local LLM](../models/deploy_local_llm.mdx) for more information.
|
||||
2. You have a knowledge base configured and the corresponding files properly parsed. See the guide on [Configure a knowledge base](../dataset/configure_knowledge_base.md) for more information.
|
||||
2. You have a dataset configured and the corresponding files properly parsed. See the guide on [Configure a dataset](../dataset/configure_knowledge_base.md) for more information.
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
8
docs/guides/agent/best_practices/_category_.json
Normal file
8
docs/guides/agent/best_practices/_category_.json
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"label": "Best practices",
|
||||
"position": 30,
|
||||
"link": {
|
||||
"type": "generated-index",
|
||||
"description": "Best practices on Agent configuration."
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
sidebar_position: 1
|
||||
slug: /accelerate_agent_question_answering
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Accelerate answering
|
||||
|
||||
A checklist to speed up question answering.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Please note that some of your settings may consume a significant amount of time. If you often find that your question answering is time-consuming, here is a checklist to consider:
|
||||
|
||||
## Balance task complexity with an Agent’s performance and speed?
|
||||
|
||||
An Agent’s response time generally depends on many factors, e.g., the LLM’s capabilities and the prompt, the latter reflecting task complexity. When using an Agent, you should always balance task demands with the LLM’s ability.
|
||||
|
||||
- For simple tasks, such as retrieval, rewriting, formatting, or structured data extraction, use concise prompts, remove planning or reasoning instructions, enforce output length limits, and select smaller or Turbo-class models. This significantly reduces latency and cost with minimal impact on quality.
|
||||
|
||||
- For complex tasks, like multi-step reasoning, cross-document synthesis, or tool-based workflows, maintain or enhance prompts that include planning, reflection, and verification steps.
|
||||
|
||||
- In multi-Agent orchestration systems, delegate simple subtasks to sub-Agents using smaller, faster models, and reserve more powerful models for the lead Agent to handle complexity and uncertainty.
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip KEY INSIGHT
|
||||
Focus on minimizing output tokens — through summarization, bullet points, or explicit length limits — as this has far greater impact on reducing latency than optimizing input size.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Disable Reasoning
|
||||
|
||||
Disabling the **Reasoning** toggle will reduce the LLM's thinking time. For a model like Qwen3, you also need to add `/no_think` to the system prompt to disable reasoning.
|
||||
|
||||
## Disable Rerank model
|
||||
|
||||
- Leaving the **Rerank model** field empty (in the corresponding **Retrieval** component) will significantly decrease retrieval time.
|
||||
- When using a rerank model, ensure you have a GPU for acceleration; otherwise, the reranking process will be *prohibitively* slow.
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip NOTE
|
||||
Please note that rerank models are essential in certain scenarios. There is always a trade-off between speed and performance; you must weigh the pros against cons for your specific case.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Check the time taken for each task
|
||||
|
||||
Click the light bulb icon above the *current* dialogue and scroll down the popup window to view the time taken for each task:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
| Item name | Description |
|
||||
| ----------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| Total | Total time spent on this conversation round, including chunk retrieval and answer generation. |
|
||||
| Check LLM | Time to validate the specified LLM. |
|
||||
| Create retriever | Time to create a chunk retriever. |
|
||||
| Bind embedding | Time to initialize an embedding model instance. |
|
||||
| Bind LLM | Time to initialize an LLM instance. |
|
||||
| Tune question | Time to optimize the user query using the context of the mult-turn conversation. |
|
||||
| Bind reranker | Time to initialize an reranker model instance for chunk retrieval. |
|
||||
| Generate keywords | Time to extract keywords from the user query. |
|
||||
| Retrieval | Time to retrieve the chunks. |
|
||||
| Generate answer | Time to generate the answer. |
|
||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user